Urinary incontinence is the loss of bladder control, a common and embarrassing problem that affects millions of people around the world every day. The frequency and severity of involuntary urination varies from occasional small leaks when you cough, sneeze or simply laugh to a complete loss of control when you feel the need to go to the toilet, resulting in you not being able to get there in time.
Unfortunately, we do not know with certainty in any country the exact number of people suffering from urinary incontinence and this is because many do not reveal their symptoms to anyone, usually because they are ashamed or believe that nothing can be done, suffering in silence.
Fortunately, things are not like that at all and today you will learn more about urinary incontinence and all the treatments and methods of treatment. And believe me, incontinence diapers will be the last solution that you can easily avoid .
How many people suffer from urinary incontinence in Greece?
Let's start a little backwards and see what's happening in the United States . In a 2017 published study on the surgical treatment of female stress incontinence and according to all the information available to the American Urological Association:
- 25% – 33% of men and women in the United States experience urinary incontinence at some point in their lives .
- More specifically, urinary incontinence is more common in women than men, with an estimated 30% of women – aged thirty to sixty – suffering from it, compared to 1.5% – 5% for men .
- About 33 million Americans have an overactive bladder that presents with the same symptoms with or without incontinence.
Unfortunately, in our country we are not very good at statistics. I tried to find an official document or a large published study but to no avail. However, according to distinguished urologists and small university studies, the situation of urinary incontinence in Greece seems to be as follows:
Where is the biggest problem located?
So if you are facing incontinence problems then you are definitely not alone . Unfortunately, urinary incontinence is not just a medical problem. It affects the emotional, psychological and social life of the patient, resulting in many people being afraid to perform the simplest daily activities, since they do not want to be too far from a toilet.
In other words, urinary incontinence can prevent people from enjoying life itself due to feelings of shame, low self-confidence, and decreased social and sexual activity.
Worst of all, more than half end up living with incontinence pads, which, in addition to the hygiene issues and medical problems they create (urinary tract infections, vaginitis and skin diseases, etc.) , lead to social isolation. Incontinence often leads to depression.
And all this while 7 out of 10 cases of incontinence can be treated or managed in more effective ways .
What are the types of urinary incontinence?
First of all, we should clarify that urinary incontinence is not a disease but a symptom of a disease or many other conditions. These are the six types of urinary incontinence:
Stress incontinence
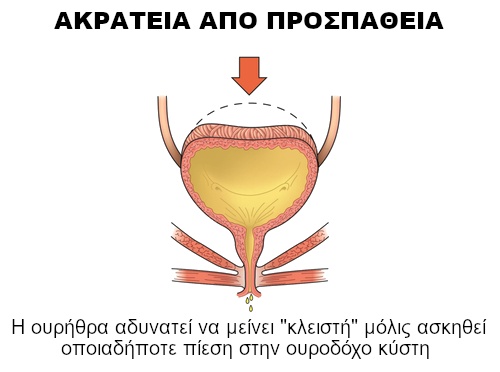
Stress incontinence is caused when pressure is applied to the bladder. The most common reasons for this usually minor leakage are:
- The cough
- The sneeze
- The laughter
- Physical exercise and any attempt to lift something heavy
Causes
Stress incontinence is the most common type of bladder control problem and occurs mainly in younger and middle-aged women. However, it often first appears during menopause. Essentially, it is caused by damage to the muscles used to control urination, such as the pelvic floor muscles and the urethral sphincter.
Thus, the most common causes of stress incontinence are:
- Pregnancy and childbirth
- Menopause, as the drop in estrogen can make the bladder muscles weaker
- Hysterectomy and similar surgeries
- Age
- Obesity
Urge incontinence
In this case, a sudden, strong urge to urinate is caused, followed by involuntary leakage of urine immediately or within a few seconds. Urge incontinence is also called overactive bladder syndrome, as control is lost as soon as someone feels the need to urinate.

Essentially, your brain is telling you that your bladder needs to empty even when it's not full. However, there are also cases where the problem is caused by your bladder muscles contracting and squeezing the bladder before it's full, causing this urgent need.
While the main symptom of urge incontinence is the sudden and irresistible need to urinate, another symptom is excessive frequency of urination during the day and night.
Causes
Overactive bladder syndrome can be caused by a mild infection or by more serious conditions. To date, the following causes of urge incontinence have been confirmed:
- Cystitis, an inflammation of the bladder
- Neurological disorders, such as multiple sclerosis, stroke, and Parkinson's disease
- Enlarged prostate, which can cause bladder prolapse and urethral irritation
Overflow incontinence
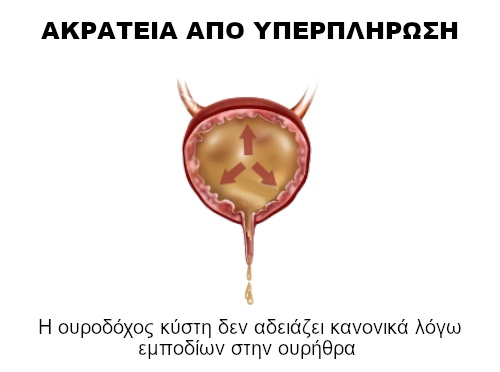
When it comes to overflow incontinence ,
- the body produces more urine than the bladder can hold, or
- is full and cannot be emptied because there is an obstruction or
- the bladder muscle cannot contract normally, thus causing leakage.
Simply put, the bladder fills without being able to empty normally, and once the pressure in the bladder becomes greater than the sphincter pressure, frequent or even continuous urine leakage occurs.
Causes
Overflow incontinence is extremely rare in women. It usually occurs in men who have prostate problems such as hyperplasia or who have undergone prostate surgery . However, diabetes and spinal cord injuries can also cause this type of incontinence.
Thus, the main causes of overflow incontinence are:
- Prostate hyperplasia
- Tumor pressing on the bladder
- Stones in the urinary tract
- Constipation
- Diabetes
- Surgery to treat urinary incontinence that went wrong
Functional incontinence
Here we are not dealing with a problem in the urinary system. Functional incontinence is caused by mental or physical disorders. That is, a physical or mental dysfunction prevents the person from reaching the toilet in time.
Causes
Typical causes of functional incontinence are:
- Arthritis and people with disabilities. Even if there are no major mobility problems, it may be very slow to remove clothes and underwear.
- The situation is similar for people who have mental retardation, with typical examples being Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia.
- Depression, anxiety, or anger can also lead some people to be reluctant to use the bathroom.
Thus, functional incontinence usually occurs in older people who, while they have normal bladder control, have another problem that prevents them from reaching the toilet.
Total incontinence
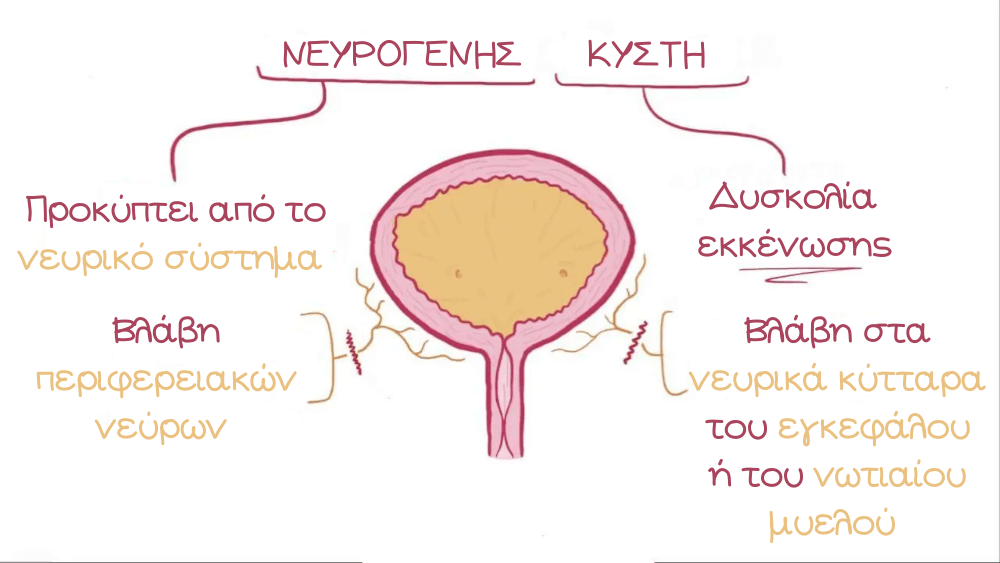
Urge incontinence is the continuous and complete loss of control over urination and is the most severe type of incontinence. It causes continuous leakage or even periodic uncontrolled emptying of the bladder contents. Essentially, in the case of urge incontinence, your bladder cannot store urine.
Causes
The main cause of total incontinence is neurogenic bladder, which causes complete loss of bladder control due to problems in the brain, spinal cord, and nervous system in general.
Usual suspects are:
- Multiple sclerosis
- Parkinson's disease
- Diabetes
- Infections of the brain or spinal cord.
- Heavy metal poisoning
- Stroke
- Spinal cord injury
- Pelvic surgery
Total incontinence can also be caused by:
- In an anatomical defect present from birth
- In a fistula (e.g. venosinus fistula)
- Urinary tract infections
Mixed incontinence
Obviously, mixed urinary incontinence is the simultaneous combination of two or more of the types of incontinence we saw.
Usually, however, it is a combination of stress incontinence and urge incontinence . Again, we encounter mixed incontinence mainly in women.
But is this temporary urinary incontinence?
Urinary incontinence is not only a result of underlying medical conditions and physical or psychological problems, but can often be caused by simple daily habits. In this case, it is not a permanent problem but a temporary urinary incontinence that can be treated very easily once we identify the source of the problem.
Causes
Certain drinks, foods, and medications act as diuretics, stimulating the bladder or increasing the volume of urine the body produces, which can lead to temporary incontinence .
- Alcohol
- Caffeine
- Fizzy drinks
- Sparkling water
- Artificial sweeteners
- Chocolate
- Hot peppers
- Foods high in spices, sugar, or acid (such as citrus fruits)
- Heart and blood pressure medications
- Sedatives and muscle relaxants or painkillers
- Large doses of vitamin C
If you suffer from temporary urinary incontinence that occurs transiently and for a short period of time, then perhaps one of the above or a combination of them is causing the problem.
Of course, temporary urinary incontinence can also be caused by an easily treatable medical condition, such as:
- Some urinary tract infection .
Most irritate the bladder, causing a strong urge to urinate and sometimes incontinence. - Constipation .
Because the rectum is so close to the bladder, it shares many nerves. Constipation causes these nerves to become overactive, resulting in frequent urination and incontinence.