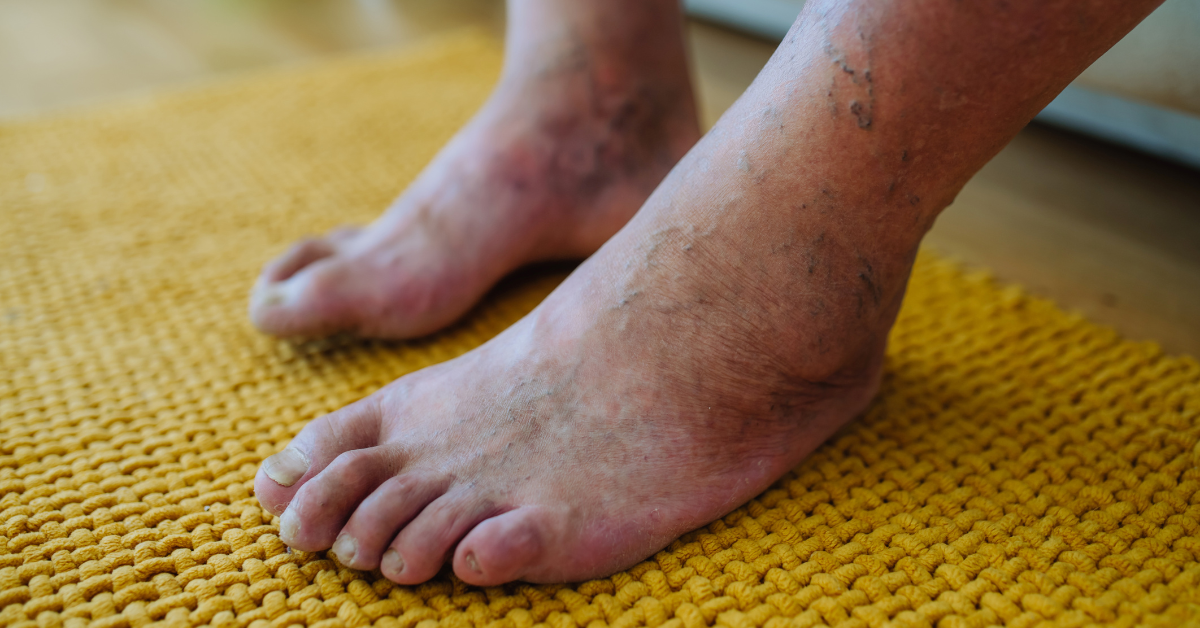
One of the most common complications that someone with diabetes can develop is diabetic foot. The term "diabetic foot" is used to describe the lesions that can be caused to the feet due to diabetes, specifically in the area from the ankle to the toes. About 15% of people with diabetes will develop diabetic foot at some point in their lives. The main causes of diabetic foot are diabetic neuropathy, which is related to nerve damage, and peripheral artery disease, which is poor blood circulation.
Symptoms that characterize diabetic foot include:
- Severe dry skin and skin complications are one of the main symptoms of diabetic foot.
- Numbness or reduced sensation in the toes (cold, heat, absence of pain).
- Blisters and calluses that can develop into ulcers if not treated promptly.
- Pain and cramps, especially when walking, which indicates peripheral artery disease.
- Hair loss on the toes or feet or changes in the nails.
- Deformation of the toes and sole.
- Bruised or discolored foot.
- Wounds or ulcers that do not heal.
How Can I Prevent the Appearance of Diabetic Foot?
According to the World Health Organization, diabetes can be managed, and its consequences, such as diabetic foot, can be prevented or delayed. It is understood that the prevention and treatment of diabetic foot is a primary concern for diabetic patients, as amputation rates are particularly high. Proper and complete management requires clinical examination and the organization of a diagnostic and therapeutic plan.
- Stop smoking. Smoking is detrimental to the health of diabetics.
- Manage diabetes with proper diet. It is important to follow the diet plan and maintain your weight within the normal body mass index range.
- Check your feet daily for any changes. Changes such as cuts, redness, swelling, wounds, blisters, calluses, or any other changes in the skin or nails.
- Keep your lower limbs clean. Diabetic foot is prone to infections. Therefore, make sure to wash your feet daily with lukewarm water.
- Choose shoes that fit your size. Shoes should fit properly and not cause any discomfort. Careful nail care is also important to avoid minor injuries.
- Schedule medical visits for check-ups. During each visit with your doctor for a complete diabetes examination, it is good to check for diabetic foot, especially if you have any nerve damage, for sensation and proper blood flow to your feet.
- Avoid walking barefoot. Always wear shoes and socks or slippers to avoid injuries or infections. Check that there are no pebbles or other objects inside your shoes and that the lining is smooth.
- Incorporate exercise into your daily routine. Movement helps with good blood circulation. Discuss with your doctor which activities are best for you and which you should avoid to not burden the condition of your diabetic foot.
- In the summer, avoid walking on hot sand barefoot as it can cause burns to your feet. Even in the sea, it is recommended to wear special shoes to avoid injuries from stones.
Diabetic ulcers are painful wounds that do not close, and their healing is quite difficult. If you have a diabetic ulcer that does not improve with treatment, you may need an amputation, i.e., the removal of the damaged toe or part of your foot to prevent the spread of infection.
Diabetic neuropathy and peripheral artery disease make wound healing particularly difficult in a diabetic foot, so the healing of a diabetic ulcer is a challenge and troubles many diabetic patients. Products that help with quick healing are your greatest ally in dealing with them.
- Clean diabetic ulcers with the colorless Prontosan Wound Irrigation Solution, which helps heal chronic ulcers by removing the biofilm that prevents the wound from healing. With Prontosan, you can also avoid ulcer infections.
- It is important to keep your wounds moist with silicone sheets like those from Askina Scar Repair for faster healing.
- Equally important is the removal of dead tissue from diabetic ulcers, as it helps prevent infections and speeds up healing. Use Prontosan Debridement Pad to remove dead tissue from ulcers easily, wherever they are on your feet.
The appearance of diabetic foot in people with diabetes can be delayed or even prevented with proper prevention. With the help of your doctor and the best ulcer care products, you can have a healthy life without the appearance of diabetic foot.