Colonized chronic ulcers are still one of the greatest challenges in medicine. In the last decade, it has become increasingly clear that the effect of antibiotic therapy is limited due to the increase of microbial tolerance. However, new, highly effective antiseptics with a broad antimicrobial spectrum are available, so topical therapy plays an important role in the treatment of chronic wounds. Polyhexanide (Polyhexamethylene Diguanide PHMB) is one of the most promising substances available today for chronic wound healing, from a clinical perspective, focusing on efficacy, safety and clinical applications. Chronic ulcers are a great burden for the patient both physically and psychologically, while hospitals incur a large financial cost for their treatment.
When Do Wounds Become Chronic Ulcers?
In the American literature, the term "chronic ulcer or wound" is defined as an opening of the skin, the healing of which takes more than 42 days or shows frequent recurrence. The delay in wound healing is mainly due to pathological factors but also to microbial infections, which hinder the healing process. A chronic wound needs therapeutic intervention in order to heal. The skin is based on continuous cell renewal, which requires the adequate transport of oxygen to the tissues and the appropriate nutrients that the body needs. The most common pathologies that increase the risk of developing chronic wounds or chronic ulcers are diabetes (diabetic foot ulcers), arterial blockages, chronic venous insufficiency (venous ulcers), reduced capillary blood flow in various parts due to pressure (bed sores), immunodeficiency and infectious diseases.
What is Polyexanide?
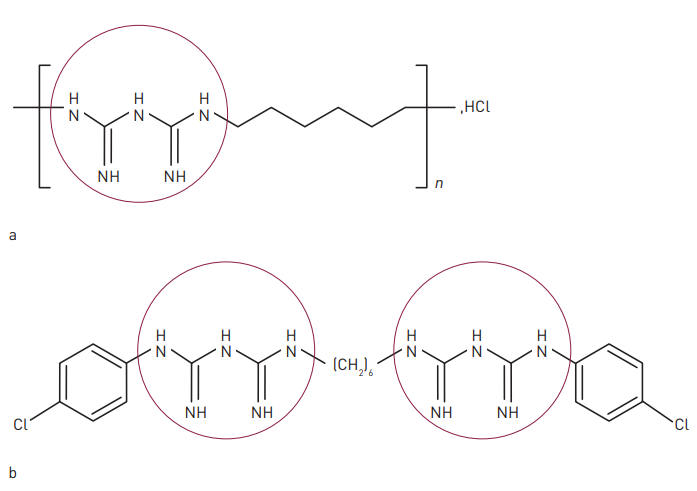
Structural formula for a) Polyexanide and b) Chlorhexidine. The chemical structure of polyhexanide is quite similar to that of chlorhexidine. It is therefore possible that polyexanide and chlorhexidine share common characteristics in terms of clinical efficacy and safety.
Polyhexanide (Polyhexamethylene Diguanide PHMB) is an antimicrobial substance suitable for clinical use in severely colonized or infected chronic or even acute wounds such as chronic ulcers. It is effective against a wide range of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, including difficult-to-control bacterial strains such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), enterococcus (VRE), and according to in vitro studies, polyexanide was able to eliminate 60-80 % of Candida albicans, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and S. aureus.
Polyhexanide has a wide range of applications, including disinfection of medical equipment and surfaces, in cosmetics, wet wipes, fabric softeners, hand and mouthwashes. It also has other types of applications such as gene delivery, DNA capture for biothreat surveillance, antibiotic filtration membranes, dental plaque control, etc.
How Does Prontosan Polyexanide Solution Help Heal Chronic Ulcers?
PHMB polyexanide wound irrigation solution such as B Braun's Prontosan® Wound Irrigation Solution contains 0.1% polyexanide as a preservative with strong antimicrobial properties and 0.1% betaine (undecyleneamidopropyl betaine) as a surfactant. Betaine has the ability to penetrate deeper surfaces and achieves more effective cleaning of the wound in contrast to water or normal saline used in similar cases for cleaning.
A major factor that hinders the healing of chronic ulcers or wounds is the presence of Biofilm. Biofilm is found in 90% of chronic ulcers and wounds.
What is Biofilm? In a nutshell, biofilm is formed by bacteria that are on the surface of the wound or ulcer and acts as a protective shield for the bacteria from antimicrobial agents. Biofilm is quite resistant to antibiotics and can release new bacteria where they create new colonization in the area of the ulcer or wound. Therefore, the threat of infections is constant and the healing process is greatly inhibited.
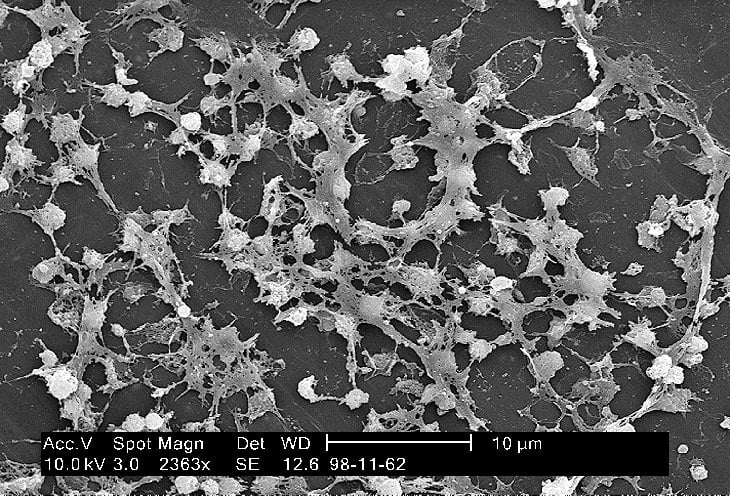

The picture shows biofilm under the microscope.
Betaine has the ability to penetrate difficult surfaces by breaking down this shield that protects the bacteria, (Biofilm). Unlike water or normal saline that just "slides' over biofilm without removing it, Polyexanide, which has a germicidal effect and attacks the bacteria, breaks down and destroys their wall, causing the cytoplasm to exit the nucleus of the bacterium and its death.
The cleansing of the wound is essential to embark on the smooth healing process. Deep cleansing of bacteria, microbial organisms and necrotic tissue is the integral and first stage of the healing process. The International Advisory Board on Wound Bed Preparation has developed a structured assessment and management tool for patients with chronic wounds, known by the acronym TIME.
Tissue Management = Removal of non-viable tissue and deep cleansing to control infections.
Inflammation & Infection Control = Reduction of Inflammation or Swelling and Bacterial Load.
Moisture Balance = Achieving optimal moisture balance in the wound area.
Epithelial Advancement = Epithelization of the skin, i.e. tissue restoration.
Sibbald RG, Leaper DJ, Queen D (2011) Iodine made easy. Wounds International 2011; 2(2). Available at: http://www.woundsinternational.com/made-easys/ iodine-made-easy
In addition to removing biofilm, Prontosan® Wound Irrigation Solution prevents its remodeling and thus stops the vicious cycle that keeps the wound chronic.
"Prontosan® Wound Irrigation Solution (0.1% Polyhexanide, 0.1% Betaine) can be combined with various dressings such as alginates and hydroins. Due to the compatibility of the tissues and the absence of irritation, it is possible to apply bandages and plasters.”
B Braun's Prontosan® Wound Irrigation Solution with Polyexanide :
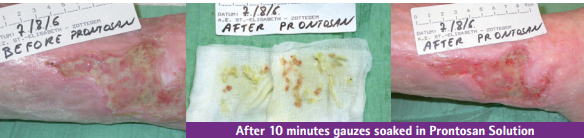
- Offers deep cleansing of the wound or ulcer.
- Prevents MD CLASS III chronic wound or ulcer infections.
- Painless wound antiseptic.
- It is dermatologically tested and does not disturb the PH of the skin.
- It balances the necessary moisture for the wound.
- It contributes to a faster and safer healing of the wound.
- It does not disturb the granulation tissue (Proliferation of new cells) which helps epithelialization and ultimately healing. This is followed by wound maturation during which the scar tissue is reorganized.
- The use of Prontosan Wound Irrigation Solution is indicated for long periods of time - There is no restriction on its use.
Polyhexanide, in a Wound Irrigation Solution, at a concentration of 0.1% has zero absorption, so it does not cause any tissue or skin irritation, is hypoallergenic, has been proven to be non-cytotoxic and does not dry out the skin and mucous membranes.
It is also worth mentioning that according to official approval by the notified Body DEKRA, the solution can be used selectively and under medical supervision in newborns and infants.
Article Sources:
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20829662/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20829658/
- https://www.mdpi.com/2077-0375/12/12/1281
- https://www.bbraun.com/en/products-and-solutions/therapies/wound-management/time-concept-wound-care.html
- https://www.bbraun.co.uk/en/products-and-therapies/wound-management/wound-bed-preparation/prontosan-faqs.html#